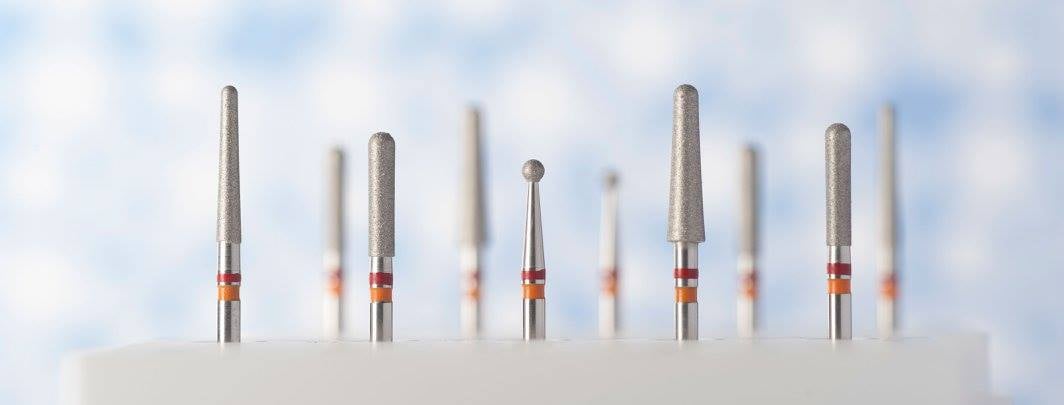
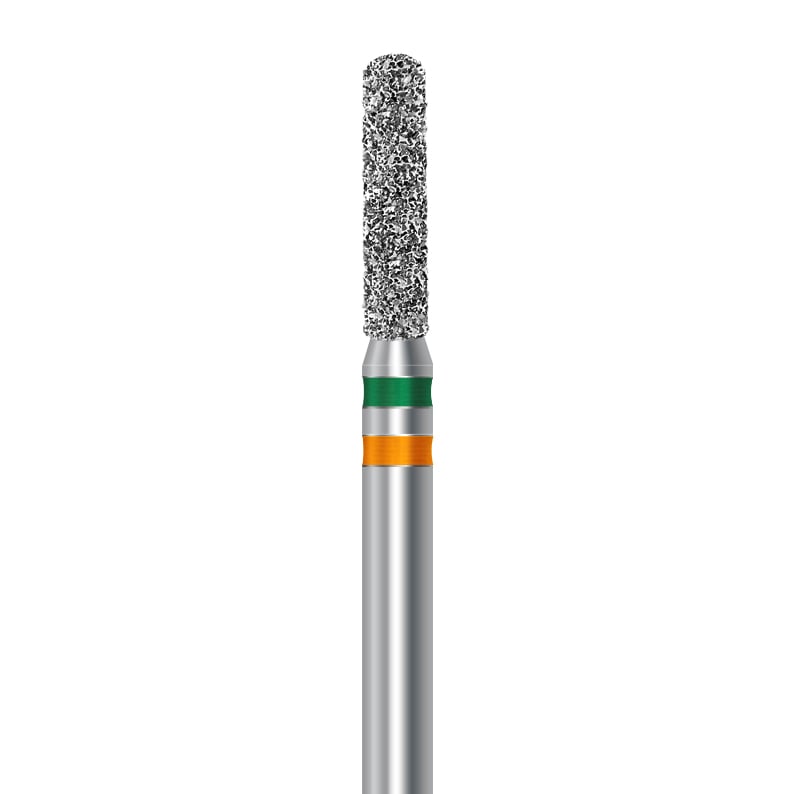
In addition to diameter, the taper is another critical parameter when understanding dental burs. Taper refers to the angle or slope of the working part of the bur. Together with the diameter, the taper influences the cutting efficiency, precision, and the specific dental procedures for which the bur is suitable. Here’s a closer look at diameters and tapers of dental burs:
- Diameter:
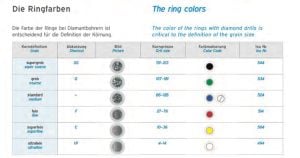
- Measurement Units: Dental bur diameters are typically measured in millimetres (mm).
- Numbering System: Burs are often numbered, and the numbering system may include information about the diameter. For example, a bur labelled as “D.856.018.FG: has a diameter of 1.8 mm (the last two digits of the number). However what’s confusing is a bur manufacturer will always give you a diameter at the widest part of the bur and not the narrowest (Tip). So the bur listed above is a tapered chamfer crown preparation bur which has a diameter at he widest part of the bur (Where the diamond starts from the shank) of 1.8mm the tip of the bur (narrowest part) will be 1.2mm.
- Taper:
- Definition: Taper refers to the angle or slope of the working part of the bur.
- Measurement Units: Taper is usually measured in degrees. Common taper values include 2, 4, 6, 8, and 12 degrees.
- Effect on Cutting Efficiency: The taper influences the shape of the cutting edge and, therefore, the efficiency and precision of cutting. Higher taper values often result in more aggressive cutting.
- Clinical Applications:
- Diameter: Smaller diameter burs are often used for fine detail work, while larger diameter burs are used for more substantial material removal.
- Taper: Different tapers are suitable for specific applications. For example, a bur with a higher taper may be used for initial tooth preparation, while a lower taper may be used for finishing and refining.
- Shank Design:
- Compatibility: The shank design of the bur (e.g., friction grip or latch-type) must be compatible with the handpiece used by the dentist.
- Standardization: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established standards for dental burs, including specifications for shank size and shapes.
- Material Considerations:
- Effect on Taper: The material from which the bur is made can influence the taper. For example, diamond burs may have different taper characteristics compared to carbide burs.

How do you workout what the taper or diameter of a bur ? follow this link Taper Calculator (omnicalculator.com)
Alternatively the best option is to contact us to help you get the correct bur for your procedure